Landslide hazard indicators
What is the Landslide Hazard Index?
The Landslide hazard is a danger category based index used by NASA to operationally provide near-real-time evaluation of potential rainfall triggered landslide events through landslide “nowcasts” (see gpm.nasa.gov/applications/landslides).
The landslide hazard indicators are called “nowcast density” and represent the number of potential days with landslide occurence for a location over a period of time for each of the 5 landslide susceptibility categories: very low, low, moderate, high, and very high.
How is it calculated ?
The method is based on NASA’s Landslide Hazard Assessment for Situational Awareness (LHASA) model that was adapted here to a long term climate change application to allow landslide risk assessments. The main difference with the original approach is a coarser resolution compatible with the use of reanalysis and climate model precipitation estimates (at 10×10 km) compared to the satellite precipitation data (1×1 km).
The LHASA model is used to provide near-real-time evaluation of potential rainfall triggered landslide hazard through landslide “nowcasts”. It is based on the combination of a landslide risk susceptibility map and a precipitation index evaluated from NASA precipitation estimates.
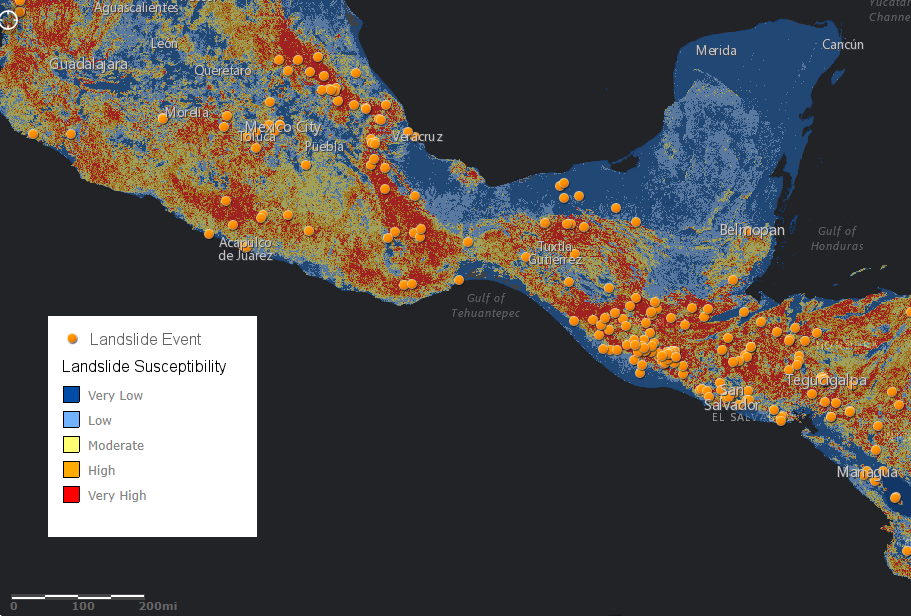
Landslide hazard susceptibility map
The susceptibility map provides a relative evaluation of static susceptibility calculated from global estimates of slope, lithology, forest cover change, distance to fault zones and distance to road networks. The susceptibility is then divided into 5 categories (very low, low, moderate, high, very high), based on decreasing area of the world occupied by each increasing class.
The Antecedent Rainfall index
In the LHASA model the potential triggering of a landslide event is characterized by a precipitation index called the Antecedent Rainfall index (ARI). The ARI is the weighted accumulation from the last 7 days of rainfall with an exponential weighting based on 949 worldwide landslides during thy year 2007–2013. The ARI index is calculated at each pixel of the susceptibility map from satellite rainfall estimations and the triggering occurs when the ARI value is above a 95th percentile threshold calculated over a reference period.
For more check the NASA Landslide Team Projects page.
How do you calculate the historical values?
Landslide hazard index values for present climate (1991-2020) are calculated using precipitation data from the ERA5-Land reanalysis. A reanalysis is produced by combining weather models with observations to provide a comprehensive description of recent global climate. The ERA5-Land dataset is provided by the Copernicus Climate Change Services (C3S) and is a world reference for historical climate analysis.
How do you calculate future values?
Landslide hazard index values for future climate (2021-2100) are calculated using our IPCC AR6 high-resolution climate projections. They are based on the recently published 6th Assessment Report (AR6) of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) simulations and obtained by statistical techniques called “downscaling” that combine reanalysis data and climate model simulations to increase the spatial resolution (from hundreds of kilometers to about ten kilometers). Our high-resolution climate projections dataset is coherent with the ERA5-Land reanalysis and allows to have future values of Landslide hazard index that are coherent with the historical Landslide index series.
Landslide hazard indicators specifications
For more details on our high-resolution IPCC AR6 Landslide hazard indicators dataset please check our Landslides dataset documentation.
